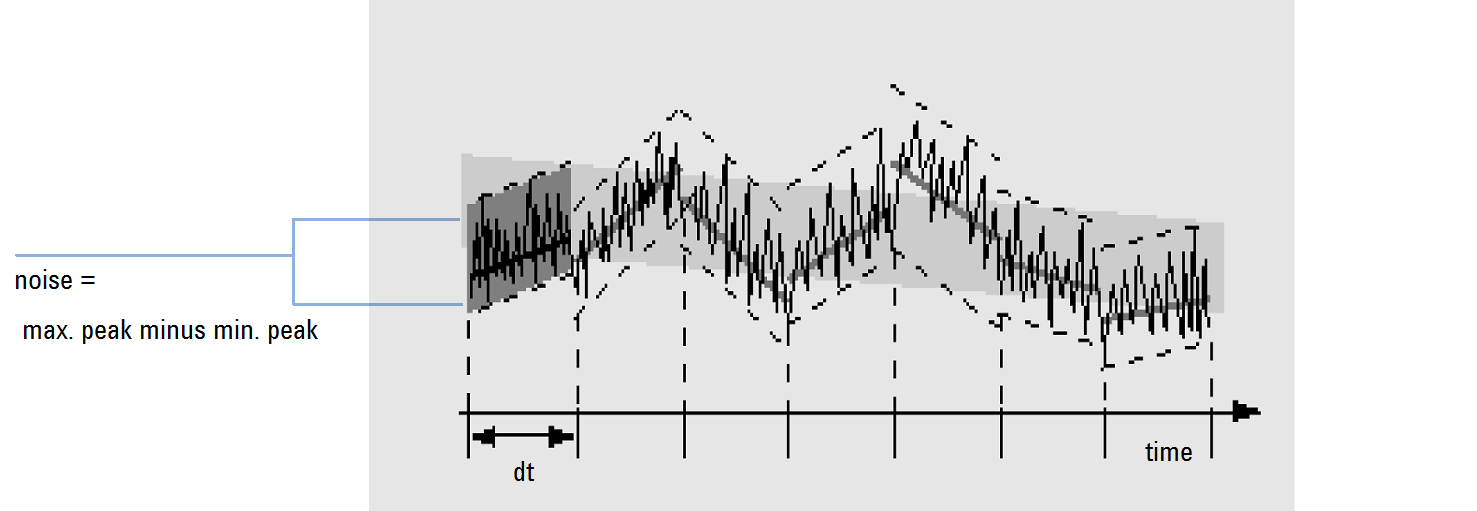
Noise calculation by the ASTM method
ASTM noise determination (ASTM E 685-93) is based on the standard practice for testing variable-wavelength photometric detectors used in liquid chromatography, as defined by the American Society for Testing and Materials. Based on the size of the time range, three different types of noise can be distinguished. Noise determination is based on peak-to-peak measurement within defined time ranges.
-
Cycle Time, t
Long-term noise, the maximum amplitude for all random variations of the detector signal of frequencies between 6 and 60 cycles per hour. Long-term noise is determined when the selected time range exceeds one hour. The time range for each cycle (dt) is set to 10 minutes which will give at least six cycles within the selected time range.
Short-term noise, the maximum amplitude for all random variations of the detector signal of a frequency greater than one cycle per minute. Short-term noise is determined for a selected time range between 10 and 60 minutes. The time range for each cycle (dt) is set to one minute which will give at least 10 cycles within the selected time range.
Very-short-term noise (not part of ASTM E 685-93), this term is introduced to describe the maximum amplitude for all random variations of the detector signal of a frequency greater than one cycle per 0.1 minute.
Very-short-term noise is determined for a selected time range between 1 and 10 minutes. The time range for each cycle (dt) is set to 0.1 minute which will give at least 10 cycles within the selected time range.
-
Number of Cycles, n
The number of cycles is calculated as:
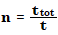
where t is the cycle time and ttot is the total time over which the noise is calculated.
-
Peak-to-Peak Noise in Each Cycle
The drift is first calculated by determining the linear regression using all the data points in the time range. The linear regression line is subtracted from all data points within the time range to give the drift-corrected signal. The peak-to-peak noise is then calculated using the formula:
N = I max - I min
where N is the peak-to-peak noise, Imax is the highest (maximum) intensity peak and Imin is the lowest (minimum) intensity peak in the time range.
-
ASTM Noise
The ASTM noise is calculated as:
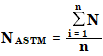
where NASTM is the noise based on the ASTM method.
An ASTM noise determination is not done if the selected time range is below one minute. Depending on the range, if the selected time range is greater than, or equal to one minute, noise is determined using one of the ASTM methods previously described. At least seven data points per cycle are used in the calculation.