Optimize sample purity settings for ASR export
See Configure LC/MS sample purity for general instructions. The following steps provide details that are relevant for ASR.
Ensure that you use an LC/MS Sample Purity method. These methods contain an MS Sample Purity section.
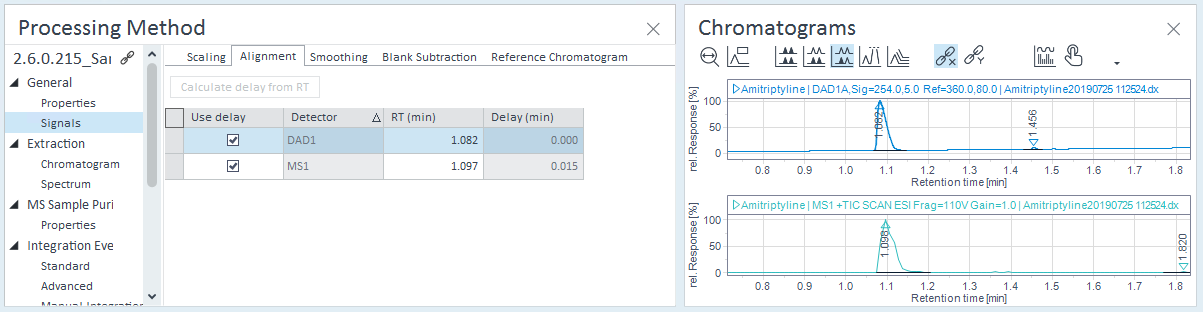
Align all signals.
Optimize integration.
Consider calculating peak purity.
Enable sample purity calculation.
Optional: Define compounds.
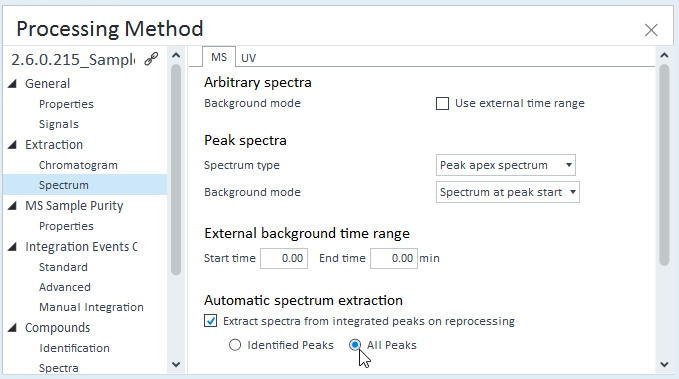
Enable automatic MS spectrum extraction for all peaks. For details, see Automatically extract MS spectra on reprocessing.
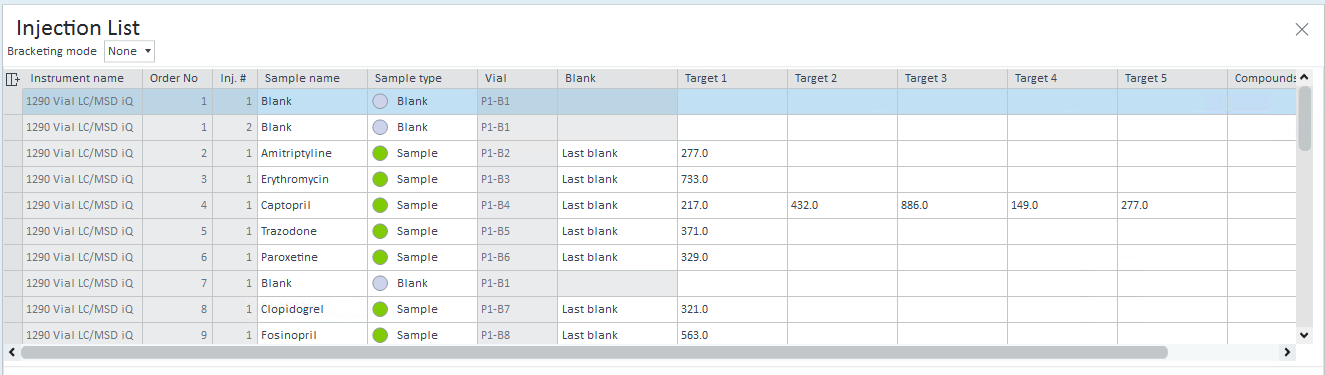
Ensure that you provided all targets in the injection list.
It is essential that peaks have the same retention time in different signals. ASR uses only the retention time to match the peaks. For details, see Align MS and UV Chromatograms.
Ensure that small peaks that could be contaminants are integrated, but baseline noise is not integrated. Optimize all signals, including all LC detectors, TICs, and EICs. For details, see Integration Optimizer.
If available, peak purity results are also exported to ASR. For details, see MS peak purity.
Check all settings, including settings for the minimum purity limit, adducts, neutral losses, and aggregates. For details, see Method: MS Sample Purity: Properties. ASR flags compounds as found or not found based on the Minimum purity limit value.
Compound identification is not required to evaluate your results in ASR. For information on setting up compounds, see Add or remove compounds or groups.
ASR mines a lot of information from MS spectra; if the spectra are not extracted, ASR may generate unexpected results.
If UV signals exist for integrated peaks, UV spectra will always be exported. UV spectra will be included in the ASR export.
You can configure targets in Data Analysis, or prepare them in Acquisition or MassHunter WalkUp Software.