What is peak identification?
Peak identification identifies the compounds in an unknown sample based on their chromatographic characteristics.
The identification of these compounds is a necessary step in quantitation if the analytical method requires quantitation. It is possible to create a valid processing method with identification even without quantitation. The signal characteristics of each component of interest are stored in the compound table of the method.
The function of the peak identification process is to compare each peak in the signal with the peaks stored in the compound table.
The identification is based on expected retention time, absolute retention time window, and relative retention time window in %. The final retention time window is the sum of relative and absolute windows, applied symmetrically to the expected retention time. The expected retention time is either specified in the method as absolute time value or calculated from a relative retention time. Time reference compounds may be used to correct the expected retention times based on possible shifts observed by specific reference compounds.
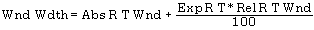
where
Abs R T Wnd | Absolute retention time window |
Exp R T | Expected retention time |
Rel R T Wnd | Relative retention time window |
Wnd Wdth | Window width |
R T Wnd = [Exp R T - Wnd Wdth; Exp R T + Wnd Wdth]
where
Exp R T | Expected retention time |
R T Wnd | Retention time window |
Wnd Wdth | Window width |
Subpages
base-id: 11013907467
id: 9007210268648459