High-Resolution Sampling
High-Resolution sampling combines the advantages of the Comprehensive 2D-LC and Multiple Heart-cutting modes, allowing the analysis of potentially unresolved peaks in the first dimension that are too broad for parking to a single sample loop. Up to 10 consecutive cuts can be created with widths down to about 2 µl, which corresponds to less than a second of ¹D retention time.
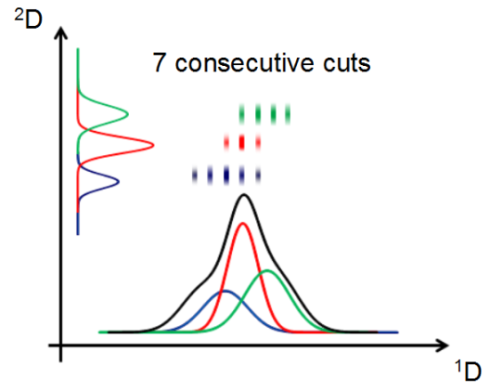
In contrast to heart-cutting mode, the entire ¹D peak can be transferred to the second dimension. This ensures that no compounds are missed, and allows precise quantitation. Peak parking is more precise than for heart-cutting, as both start and end of a cut are clearly defined; heart cutting, on the other hand, determines cuts by switching the valve only at the end of a cut. As in multiple heart-cutting, the second dimension is decoupled from the first dimension using parking decks with sample loops; this allows long gradients and a high resolution in the second dimension.
In contrast to full comprehensive mode, where consecutive cuts can take, for example, 30 seconds, the ¹D resolution is retained with high-resolution sampling.
Multi-Inject
If High-Resolution data is acquired in multi-inject mode, then the respective series of cuts of all applicable sample loops per deck valve is injected subsequently and then analyzed in one second dimension separation. So, instead of a single ²D chromatogram per cut, there is just one ²D chromatogram for all cuts that are analyzed together in each multi-inject series. That is, if a high-resolution series uses two deck valves, this will result in two ²D chromatograms.
The separate cuts of a multi-inject series are displayed in the Sampling Table and annotated in the ¹D chromatogram. But, in the Contour Plot and Diagnostic Signals windows of the second dimension, the multi-inject run is displayed as one cut run.
base-id: 10237061515
id: 10237061515