Properties of a 2D peak
¹D retention time
A 2D peak may consist of multiple assigned peaks in the cut signals of the corresponding cut series.
A peak in a cut signal has a ¹D retention time:
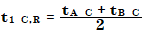
where
t1C,R | ¹D retention time of single peak in a cut signal |
tA C | Cut peak start time |
tB C | Cut peak end time |
The ¹D retention time of the resulting 2D peak is then calculated as a weighted average by area of the cut ¹D retention times:
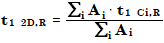
where
t1 2D,R | ¹D retention time of 2D peak |
A | Area |
i | Cut number |
t1 Ci,R | ¹D retention time of single peak in a cut signal |
²D retention time
Same as for the ¹D retention time, the ²D retention time of a 2D peak is calculated as the weighted average by area of the cut ²D retention times:
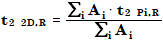
where
t2 2D,R | ²D retention time of 2D peak |
A | Area |
i | Cut number |
t2 Pi,R | ²D retention time of the ith peak. |
Area
The area of a 2D peak is calculated as the sum of the areas of all associated cut peaks.
Height
The height of a 2D peak is the height of the associated cut peak with the largest height.
base-id: 10237279243
id: 10237279243