Injection List
What do you want to do?
Injection List in Data Processing view
This window displays all selected single sample injections or injections that are part of the selected result set in the navigation tree. The data selection in this window is synchronized with the injections selected in other windows (for example, the Chromatograms window).
The window is divided in two parts:
The upper part contains the list of injections.
The Compound amounts tab in the lower part contains information on compound specific amounts in calibration standards (see also Use different amounts per compound and injection). You can expand or collapse the Compound amounts tab.
The Fraction target masses tab in the lower part contains information related to mass-based fraction collection. The tab is only visible if fraction target masses have been overridden in the acquisition method.
You can also set up a bracketed calibration in this window (see Set up a bracketed calibration).
Instrument name | Name of the instrument with which the data has been acquired. The instrument name is available for data acquired and saved with OpenLab CDS v2.6 or higher. It may not be available for older data. |
Order # | Order number of the sample in the sequence (sequence line). |
Injection # | Injection # of total number of injections per sample. |
Sample name | Sample name of the injection as entered in the sequence. |
Sample label | Sample label of the injection (optional). Can be used, for example, to search for data in the Data Selection view, or to group data in a report template. Only alphanumeric characters are allowed. |
Sample type | Sample types are used in a sequence to describe each item being processed. Sample type descriptions:
|
Bracket | Shows how calibration standards are bracketed according to the selected Bracketing mode. |
Run type | For calibration standards: Clear all calibration means that all previous calibration points will be removed when processing this standard. Clear calibration at level means that all previous calibration points of the level of the calibration standard will be removed when processing this standard. Empty means that a new point will be added to the calibration curve. If a calibration point already exists for the current calibration level, and you use average values to calculate the calibration curve, the application calculates the average value of all existing calibration points for the given level (see Modes of using individual points). |
Level | For calibration standards: level of the standard. |
Injection date | Date and time when the sample was injected. |
Modification date | Date when the injection was last processed. |
Sample Amount | Sample amount as entered in the sequence. |
ISTD Amt 1-5 | ISTD amounts as entered in the sequence table. They can be modified for a individual injections afterwards. ISTD Amt 1 to ISTD Amt 5 are automatically mapped to multiple ISTD compounds in the order of their expected retention times. |
Multiplier 1-5 | Sample multipliers; multiplication factors as entered in the sequence table per sample, can be modified for a single injection afterwards. Used to calculate the concentration for all compounds (see Concentration and mass% and Correction factors) |
Dil. Factor 1-5 | Sample dilution factors; dilution factors as entered in the sequence table per sample, can be modified for a single injection afterwards. Used to calculate concentration for all compounds (see Concentration and mass% and Correction factors) |
Acq. method | Name of the method used to acquire the raw data (acquisition method). |
Proc. method | Name of the method used to analyze the data (processing method). |
Description | Description of the sample as entered in the sequence table. |
Vial | Vial number or plate location. |
Injector position | Position of the injector on the instrument. For dual tower GC instruments: front or back. For LC: always front. |
Data file | Name of the data file if source system is file based. |
LIMS ID 1-3 | Keys required for connection from and to a LIM system. |
Barcode | Barcode label as it has been read from the sample vial. The value is read only. |
Expected Barcode | The expected barcode as provided in Acquisition (manually or via barcode scan). When you automate your processes, you can determine actions if the expected barcode does not match the actual barcode (e.g. abort the sequence). The value is read only. |
Compound amounts | Indicator if the amount of a calibration sample has been modified. The compound amount is defined in the calibration parameters in the method, but may be adjusted for individual injections. The Compound amounts tab is shown in the lower part of the Injection List window. It shows the amounts defined in the method and allows editing of the actual amounts in the sample. |
Target 1-5 | For mass spectrometry: Masses or formulas that you want to use for the MS sample purity calculation. You can mix molecular weights and formulas, for example: Your entry will be checked for positive molecular weights, and for letters that represent existing chemical elements. If you add target masses or formulae, and you link your injection to a mass spectrometry method, the processing function will automatically generate extracted ion chromatograms (EICs). If the target masses correspond to any available selected ions, it will also extract selected ion monitoring (SIM) signals.
|
Compound custom fields | If you have configured Compound Custom Parameters for your project: Click in the Compound custom fields column to show the corresponding parameters and values in a separate part of the window. If you have configured Sample Custom Parameters for your project, there will be a separate column for each single parameter. Compound custom fields are configured per project in the Control Panel. There you also define if a custom parameter is mandatory. Values of mandatory parameters cannot be deleted. Parameter values can also be modified in Acquisition. |
Blank | Select which blank to subtract from the signal of an injection (see Configure processing method for blank subtraction). By default, the blank last acquired prior to the injection is selected. The blank can only be selected if: Blank subtraction is turned on in the processing method The sample is not a blank itself The option Use blanks defined in the sequence is selected in the processing method |
Compound amounts tab
Type | The icon indicates whether it is internal or external standard, a normal or time reference compound, or a group compound.
External standard, normal compound
External standard, time reference compound
Internal standard, normal or time reference compound
Named group
Timed group |
Name | Name of the compound
|
Corrected amount | Calculated from compound amount in sample, sample-specific compound multipliers, and sample-specific compound dilution factors. The dilution factors are used either as a divisor or as another multiplier; you choose this calculation with the Concentration and corrected amount calculation setting in the processing method under Calibration on the General tab. |
Amount in sample | Overrides the compound amount set in the processing method. Amount in sample can also be set in Acquisition. |
Amount in method | Read only: Compound amount defined in the processing method |
Is ISTD | Read only: Shows whether the compound is an internal standard. This column is only visible if you enabled internal standards in the processing method. |
Multiplier 1 - 5 | Sample-specific compound multipliers; these multipliers are used to calculate the corrected compound amount. |
Dil. factor 1 - 5 | Sample-specific compound dilution factors; these dilution factors are used to calculate the corrected compound amount. |
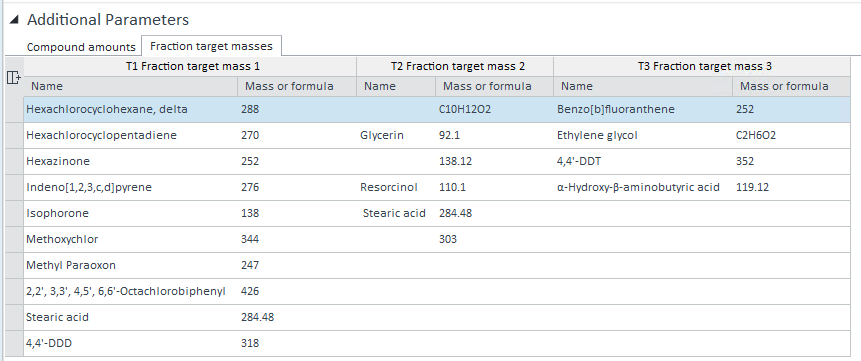
Fraction target masses tab
The Fraction target masses tab is only visible if you have overridden fraction target masses in the sequence or single sample prior to starting the run. Each method override column in Acquisition may contain up to ten name/mass pairs, separated by semicolon. The Fraction target masses shows the name/mass pairs using a tabular format.
T1 Fraction target mass 1 | Shows the content of an overridden SQ: T1 Fraction target mass 1 column in the sequence table or single sample. |
T2 Fraction target mass 2 | Shows the content of an overridden SQ: T2 Fraction target mass 2 column in the sequence table or single sample. |
T3 Fraction target mass 3 | Shows the content of an overridden SQ: T3 Fraction target mass 3 column in the sequence table or single sample. |
Subpages
base-id: 11012235147
id: 18014409521717131