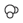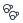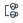Compound Table tab
Order number | Order number of compound (as sorted by retention time). The order number cannot be edited. |
Type | The icon indicates whether it is internal or external standard, a normal or time reference compound, or a group compound.
External standard, normal compound
External standard, time reference compound
Internal standard, normal or time reference compound
Named group
Timed group |
Name | The name of the compound. |
Signal | The detector signal used to identify and quantify the compound. The drop-down list offers the names of all signals that are currently shown in the Method Selector or have been used in the method during the current session. The list of signal names is independent of the instrument driver. Note: Changing the signal setting for a compound may remove the calibration curve. If you discard the calibration curve, you will need to rebuild the calibration curve with a calibration standard using the new signal. If you want to keep the calibration curve, see Move calibration curve to another signal |
Is time ref. | Set the compound as a time reference compound. See Use time reference compounds in the General tab. Time reference compounds will always be identified based on the expected retention time. |
Associated time ref. | Name and signal of the time reference compound that is associated with the current compound. See Use time reference compounds in the General tab. For the time reference compound, the difference between expected and actual retention time is calculated. This shift value is then used to correct the expected retention time of the current compound or the start and end time of a timed group. For details on the calculation, see Calculations for time reference compounds. |
Factor | Factor applied to the shift that is calculated for the time reference compound. See Use time reference compounds in the General tab. It is a percentage value by which you can define the extent of correction. For details on the calculation, see Calculations for time reference compounds. |
Is RRT ref. | Set the compound as an RRT reference compound. |
Associated RRT reference | Name and signal of the RRT reference compound that is associated with the current compound. See Calculations for relative retention times (RRT). |
Exp. RT | The retention time in minutes where the compound is expected. See Evaluation of the retention time window. |
RRT | Relative retention time (RRT). You typically enter an RRT value from the literature. The expected retention time of the compound is then updated. Also vice versa, if you change the expected retention time, the RRT value is updated. See Use relative retention times (RRT). |
Absolute RT Window (min) | The window in minutes around the expected retention time that defines the range in which the compound will be identified. See Evaluation of the retention time window. |
Relative RT Window (%) | The window in percent (%) around the expected retention time that defines the range in which the compound will be identified. See Evaluation of the retention time window. |
Response Window Type | Mass spectrometry: Shows how the response window of a qualifier ion is interpreted. For example, the target ion has a response of 50 % , and the qualifier ion has a response percentage of 20 % . The response window for the qualifier is then calculated as follows: Absolute: The response of the qualifier ion must be between 30 % and 70 % of the target ion response. Relative: The response of the qualifier ion must be between 40 % and 60 % of the target ion response. |
RT Update | You can define if and when the system replaces the expected RT in the method by a corrected RT. With time references, an additional general factor is used in the formula. For details on the calculation, see Calculations for updating retention times. You can choose between the following modes for updating the expected RT:
|
RT Update Factor (%) | The extent of correction, used to calculate a corrected retention time. See RT Update. |
Peak match | This setting is relevant if there is more than one peak in the retention time window. Here, you define which of the peaks should be considered for the given compound. See Conflict resolution. |
 If you installed the 2D-LC Add-on, the Compound Table contains more information. See 2D-LC help on the compound table for details.
If you installed the 2D-LC Add-on, the Compound Table contains more information. See 2D-LC help on the compound table for details.
See Also
base-id: 11012967179
id: 9007210267708171